Manufacturing leaders constantly seek efficient, cost-effective cleaning solutions to meet demanding production schedules while maintaining quality standards and environmental compliance. But how do aqueous cleaners perform in high-volume manufacturing environments?
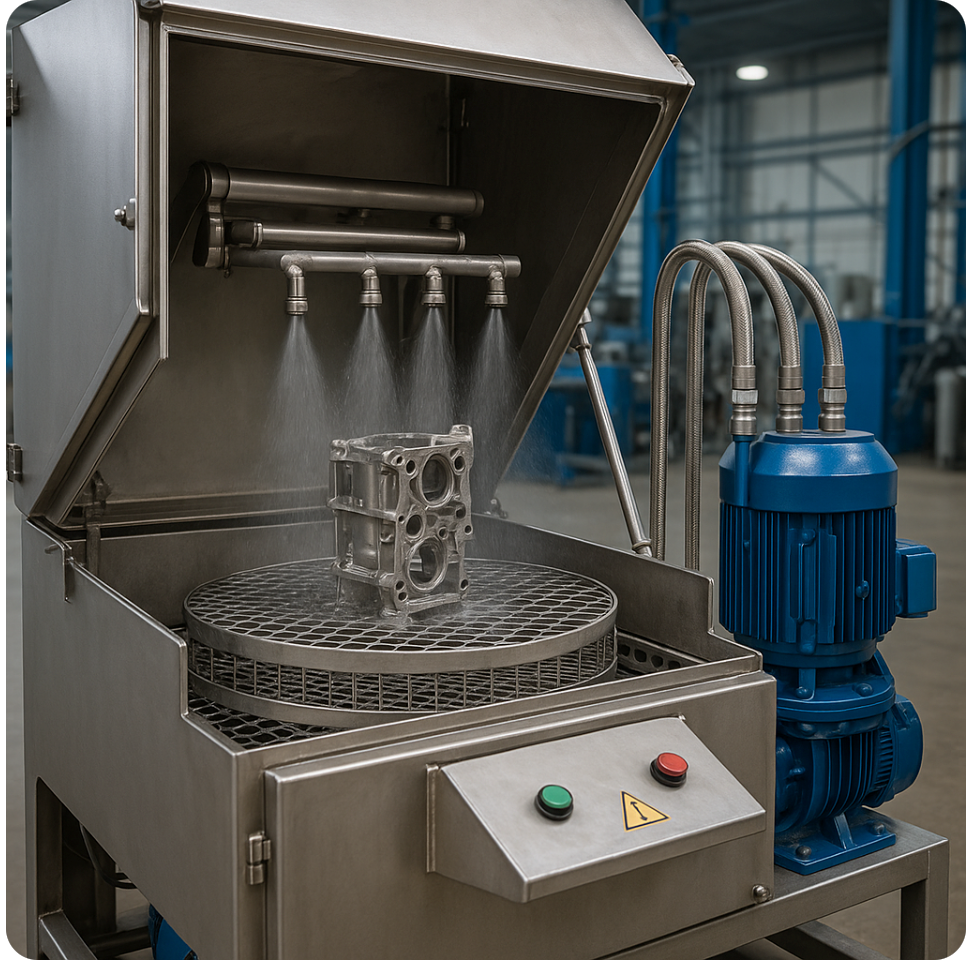
Aqueous cleaners perform exceptionally well in high-volume manufacturing, consistently achieving 95-99% cleaning effectiveness while processing up to 1,000 parts per hour in automated systems, with significantly lower operating costs than solvent-based alternatives.
While this performance data is impressive, it’s important to note that these results can vary significantly based on specific applications, part geometries, and contamination types. Understanding these variables and how they affect cleaning performance will help you determine if aqueous cleaning is the right solution for your manufacturing needs.
What Factors Affect Aqueous Cleaning Performance In Manufacturing?
The effectiveness of aqueous cleaning systems depends on four key variables: temperature, cleaning chemistry, mechanical action, and time. Temperature typically needs to be maintained between 140-180°F for optimal performance, as heat helps break down oils and other contaminants while accelerating chemical reactions.
The choice of cleaning chemistry is crucial and must be matched to the substrate material and the type of contamination removed. For example, alkaline cleaners remove organic soils and oils well, while acidic solutions are better suited for removing rust and scale.
Mechanical action, whether through spray pressure, ultrasonic cavitation, or agitation, helps dislodge contaminants from part surfaces. The level and type of mechanical action needed varies based on part geometry and contamination severity.
How Do Environmental Regulations Impact Aqueous Cleaning Implementation?
Environmental regulations have become increasingly stringent regarding industrial cleaning processes, particularly concerning VOC emissions and waste disposal. Aqueous cleaning systems generally face fewer regulatory hurdles than solvent-based alternatives but still require proper wastewater management and disposal protocols.
Many facilities need to implement water treatment systems to handle the cleaning solution discharge, including oil separation, filtration, and pH adjustment. However, these treatment systems often allow for water recycling, reducing water consumption and operating costs.
What Are The Cost Considerations Of Operating Aqueous Cleaning Systems?
Initial investment in aqueous cleaning systems can be higher than traditional solvent-based systems, primarily due to the need for heating equipment, filtration systems, and water treatment infrastructure. However, operating costs typically decrease over time due to reduced chemical costs and fewer regulatory compliance expenses.
Energy consumption is significant; maintaining elevated temperatures requires constant heating. However, modern systems often incorporate heat recovery and insulation features to minimize energy loss. Additionally, recycling and reusing cleaning solutions help offset water and chemical costs.
Maintenance costs should also be considered, including regular system cleaning, solution monitoring, and filter replacement. These costs are generally predictable and can be effectively managed through proper preventive maintenance scheduling.
How Does Automated Aqueous Cleaning Compare To Manual Processes?

Automated aqueous cleaning systems significantly outperform manual cleaning processes in terms of consistency and throughput. While manual cleaning might process 20-30 parts per hour, computerized systems can handle hundreds or even thousands of parts in the same timeframe, with minimal variation in cleaning quality.
Automation also reduces labor costs and potential worker exposure to cleaning chemicals. Modern systems can be integrated into existing production lines, creating a seamless workflow that minimizes handling and transporting parts between processes.
However, automated systems require careful programming and monitoring to maintain optimal performance. Parameters such as wash cycles, rinse stages, and drying times must be precisely controlled to achieve consistent results across different part types and contamination levels.
What Maintenance Requirements Should Manufacturers Expect With Aqueous Systems?
Regular maintenance is crucial for maintaining the efficiency and longevity of aqueous cleaning systems. Daily tasks typically include monitoring solution concentration levels, checking filtration systems, and inspecting spray nozzles or ultrasonic transducers for proper operation.
Weekly or monthly maintenance often involves cleaning or replacing filters, removing accumulated sludge from tanks, and checking heating elements and pump systems. Solution chemistry should be regularly tested and adjusted or replaced to maintain optimal cleaning performance.
Most manufacturers find that implementing a preventive maintenance schedule reduces unexpected downtime and extends equipment life. This typically includes quarterly deep cleaning of tanks and processing equipment, annual replacement of significant wear components, and regular calibration of control systems.
Taking The Next Step With Aqueous Cleaning
Before implementing an aqueous cleaning system in your high-volume manufacturing operation, conduct a detailed process audit to identify your specific cleaning requirements, including part geometries, contamination types, and production volumes. This analysis will help you select the most appropriate system configuration and cleaning chemistry for your needs, ensuring optimal performance and return on investment.